Estimated reading time: 4 minutes
What is Posture Guard?
Posture Guard is the new managed Cyber Security service offered by Secure Online Desktop to protect companies from cyber attacks and data breaches. It is a cutting-edge solution that uses continuous Breach Attack Simulation (BAS) techniques to constantly evaluate an organization’s security posture and identify potential vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by hackers.
The Posture Guard service is based on sophisticated ethical hacking techniques performed in a controlled way to test a system’s ability to withstand simulated intrusion attempts. This makes it possible to identify security weaknesses before they become a real threat.
How Posture Guard Works
Posture Guard uses attack methodologies similar to those used by cybercriminals to penetrate an organization’s defenses. However, unlike a real attack, Posture Guard is a benign tool used solely for defensive purposes.
The service involves the periodic execution of simulated penetration tests to identify exploitable vulnerabilities in the customer’s systems and networks. These tests are conducted in a controlled manner to avoid any damage, but realistically reproduce the techniques used by ill-intentioned attackers to breach a system’s security.
The test results provide detailed information on the flaws identified, allowing the customer to quickly fix them before they can be exploited in a real attack. In this way, Posture Guard helps drastically reduce the risk of a data breach.
The Benefits of Posture Guard
Posture Guard offers numerous advantages over traditional security solutions, including:
- Proactive vulnerability detection – Posture Guard doesn’t just monitor and react to threats, but actively looks for exploitable weaknesses. This makes it possible to correct security flaws before hackers target them.
- Continuous improvement – Periodic testing allows you to measure and improve an organization’s security posture over time. You can tangibly see the positive impact of countermeasures applied.
- Realistic approach – By simulating real attacks, you get a concrete assessment of how well a system is actually protected against real-world threats.
- Cost savings – Finding and fixing vulnerabilities ahead of time prevents data breaches that would involve substantial costs for system restoration, legal sanctions, and reputation damage.
- Regulatory compliance – Many regulations require regular penetration testing. Posture Guard helps continuously meet such requirements.
Monitoring Security KPIs

An advanced feature of Posture Guard is the continuous monitoring of key security Key Performance Indicators (KPI) to keep track of a client’s system security status.
Real-time data is collected and analyzed on metrics such as:
- Number of critical vulnerabilities identified
- Changes over time in attack surfaces
- Detection rate capabilities of security solutions
- Incident response times
- Compliance with standards and policies
The status of these metrics is communicated to the client through dashboards and periodic reports. In the event of negative changes indicating a potential security deterioration, real-time alerts are sent.
This enables quick intervention to investigate and mitigate possible issues before they become a concrete threat, keeping the risk level always under control.
For example, a drop in the detection rate of simulated attacks by a network protection solution likely signals a malfunction or misconfiguration that requires urgent investigative and corrective actions. Constant KPI monitoring makes it possible to promptly identify these situations.
Conclusions
Posture Guard represents the evolution of managed Cyber Security, which no longer just protects systems but adopts a proactive approach to continuously improve security posture.
The combination of regular simulated penetration tests and continuous monitoring of key KPIs makes it possible to identify and resolve vulnerabilities before attackers can exploit them.
For companies that want to adopt enterprise-level Cyber Security without having to manage complex internal ethical hacking activities, Posture Guard is the ideal solution to effectively protect their data and systems.
Useful links:
Tempo di lettura stimato: 6 minutes
Today we are talking about the CTI update of our services. Data security is an aspect that must always be taken into consideration to prevent data from being stolen in any way.
Network problems
When you have a presence connected to the network, especially if it contains sensitive data, the potential threats to which you are exposed are manifold. The theft of your customers’ data, in fact, is only one of the potential negative situations that can arise and that could compromise the solidity of your site and the reputation of your company.
The Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) service, was created with the aim, not only of discovering which areas are most at risk, but also of preventing targeted attacks. Prevention represents the right solution thanks to which it is possible to avoid that the situation can become difficult to deal with and that there may be future complex problems to be solved.

CTI: preventive-threat analysis
Thanks to the CTI service we offer and our Cyber Treath Hunter , it is possible to prevent a planned attack hits. The search for vulnerable areas of the IT infrastructure represents the first process of the CTI service we propose.
This information, in fact, is that which is processed in the Dark Web , where most of the design of the attacks. The analysis of data leakage, therefore, is carried out with extreme care to understand what and how much data may have become the object of hacker attention . Consequently, we can also understand what specific attack targets or upcoming information at risk may be.
The various analyzes are carried out with care and precision, to avoid that vulnerabilities are exploited and the security of the structure jeopardized. Thanks to the analysis carried out by a team of professionals, your company will prevent attacks from hitting you and triggering economic and image problems .
The analyzes carried out by Cyber Threat Intelligence
As regards the different phases of the analyzes proposed by us, these are carried out in a particularly accurate manner. We practice a series of procedures thanks to which it is possible to identify what are the potential threats that may be present in the network.
Let’s look at these steps to understand how we go about offering a complete service to our customers.
Global-data analysis
After having hypothesized the type of threat to be avoided, then the necessary data that must be analyzed, the team of technicians in charge takes care of carrying out a series of information gathering procedures. Thanks to this we can understand if the necessary data are well protected or at risk of breach . Basically we try to think like hackers before they prepare for the attack.
The data are subjected to careful analysis and above all are adequately divided. This procedure was created to simplify the phase of studying the data themselves , thus preventing an accumulation of information that could lead to confusion during the analysis phase.
The data and the second-analysis, between fundamental and secondary information
Once the information gathering phase is complete, we move on to the initial analysis of the same. With this fundamental step it is possible to eliminate all the information deemed superfluous leaving space for those that have greater relevance in the study phase.
At this point, the data analysis phase takes place, the purpose of which is to actually understand what concrete threats to avoid can be.
During the study phase it is decided which are the different procedures to be adopted on the infrastructure to prevent attacks from being successful. Through these analyzes, we can then decide precisely how to further increase corporate data defenses.
The choice of security-measures to be adopted
Finally, there is the implementation of security practices with a specific task: to make the analysis results operational.
Here’s how, thanks to this set of procedures, the CTI service we offer is incredibly useful to avoid potential problems. We remind you that even a single attack carried out can have a significant impact in economic terms.
Prevention of future-attacks
Thanks to this set of CTI analyzes, you can, therefore, prevent future attacks. Our team is not only concerned with analyzing potential and future threats, but also those that may be based on the current situation of the IT infrastructure.
We want to underline, in fact, how constant threats are subject to rapid evolution and how important it is to always be adequately protected and prevented. With services like SOCaaS and CTI, we securely monitor the corporate network making sure it remains safe and healthy.

CTI: The importance of maximum-online-security
We therefore encourage you to consider these security risk situations as less remote than you might think. These same situations can be the cause of a series of breaches and data losses that can compromise the company.
Thanks to our SOCaaS, and especially the CTI. it is possible to avoid that the data present on the corporate network can be easily intercepted.
Understanding what the threats are, having a detailed report and above all analyzing the countermeasures that must be adopted is our task and thanks to our state-of-the-art systems we offer a complete service capable of putting the infrastructure in total safety.
Our services cover many security risk situations and we generally offer many professional solutions for companies. The SOCaaS, with system SIEM and UEBA, as well as CTI and
Keeping safety always on top is our job, if you want more information, don’t hesitate to contact us!
Useful links:

Estimated reading time: 5 minutes
Cyber Threat Hunting is a proactive security search across networks, endpoints and datasets to hunt down malicious, suspicious or risky activities that have escaped detection by existing tools.
Definition
There is a distinction between malware detection and cyber threat hunting . Threat detection is a passive approach to monitoring data and systems to identify potential security problems. However, it is a necessity and can help a threat hunter . Instead, proactive threat hunting tactics have evolved to use new threat intelligence on previously collected data to identify and classify potential risks before the attack .
Security personnel cannot afford to believe that their security system is impenetrable. Must always remain vigilant for the next threat or vulnerability . Rather than sitting around and waiting for threats to strike, cyber threat hunting develops hypotheses based on knowing the behaviors of threat actors and validating those hypotheses through active research in the environment .
With threat hunting, an expert doesn’t start with an alarm or indicators of compromise (IOC), but with deeper reasoning. In many cases the threat hunter’s efforts create and concretize the alarm or the IOC.
This aggressively assumes that a breach has occurred or will occur at the company. Security officers hunt down threats in their environment rather than rely on automatisms.

Threat hunting practice
For companies that are ready to take a more proactive approach to cybersecurity , which tries to stop attacks before they get too deep, adding threat hunting protocols to their security program is the next logical step.
After consolidating endpoint security and incident response strategies to mitigate the now unavoidable known malware attacks, companies can begin to take the offensive . This means digging deep and finding what hasn’t been detected yet. This is precisely the purpose of cyber threat hunting.
As mentioned earlier, threat hunting is an aggressive tactic that starts from the premise of the “assumption of violation”. Attackers are already inside an organization’s network and are secretly monitoring and moving into it.
This may sound far-fetched, but in reality, attackers can be inside a network for days, weeks, and even months . In the meantime, they prepare and execute attacks as advanced persistent threats, with no automatic defense detecting their presence . Cyber threat hunting stops these attacks by looking for covert indicators of compromise (IOCs) so they can be mitigated before the attacks reach their goals.

The key elements of a threat hunting
The goal of the threat hunt is to monitor daily activities and traffic across the network and investigate possible anomalies to find any undiscovered malicious activity that could lead to a complete breach . To achieve this level of proactive detection, threat hunting incorporates four equally important components.
1. Methodology
To be successful in hunt for threats, companies must commit to a proactive, full-time approach that is continuous and evolving. Instead, a responsive, ad hoc implementation, “ when we have time “, will be self-defeating and will only lead to minimal results.
2. Technology
Most companies already have comprehensive endpoint security solutions with automatic detection. Threat hunting works in addition to these and adds advanced technologies . The aim is to find anomalies, unusual patterns, and other traces of attackers that shouldn’t be in systems and files.
The new cloud-native endpoint protection (EPP) platforms that leverage big data analytics can capture and analyze large volumes of non-data filtered on endpoints, while behavioral analytics and artificial intelligence can provide broad, high-speed visibility into malicious behaviors that seem normal at first.
3. Highly qualified and dedicated staff
The threat hunters are a race of their own. These experts know how to use the security technology deployed by companies. In addition, also combine the aspiration to go on the offensive with intuitive problem-solving skills to uncover and mitigate hidden threats.
4. Threat intelligence
Having access to evidence-based global intelligence from experts from around the world (e.g. Miter Att & amp; ck ) further improves and accelerates hunting for existing threats. Hunters are aided by information such as attack classifications for identifying malware and threat groups , as well as advanced threat indicators.

The abilities of a threat hunter
The Threat Hunting Report from Crowd Research Partners confirms the importance of certain capabilities for threat hunting. When asked to rank the most important skill, the survey found that:
69% chose threat intelligence
57% chose behavior analysis
56% chose automatic detection
54% chose machine learning and automated analysis

The profile of a threat hunter
Threat hunters look for attackers who manage to break through vulnerabilities that a company might not even know exist . These attackers spend a considerable amount of time planning and performing the reconnaissance, acting only when they know they can successfully penetrate the network without warning. They also inject and build malware that has not yet been recognized or use techniques that do not rely on malware at all, to provide a persistent base from which to attack.
What does it take to outsmart even the smartest attackers?
A cyber threat hunter is relentless and can find even the smallest trace of what attackers have left behind. In general, threat hunters use their skills to undo the small changes that occur when attackers make their moves within a system or file.
The best threat hunters rely on their instincts to sniff out the stealth moves of the most dangerous attacker.
Are you a threat hunter? Contact us!
SOD is looking for a SOC / ICT analyst to add to the team. If you think you’re the right person, visit this page to view the detailed job posting.
Useful links:
Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) – greater effectiveness for IT security
Long-term search: what’s new in the SOCaaS service




A SIEM solution in IT is one of the essential components of a SOC (Security Operation Center). Its task is to collect information and analyze it in search of anomalies and possible breaches in the system. But the defense process hasn’t always been that simple. What we now call SIEM, Security Information and Event Management, is the union of two different types of cyber security tools.
SIM and SEM: the origins
Before the arrival of a complete SIEM solution in computing, security was heavily focused on perimeter security and did not keep the internal network adequately controlled. The first solutions developed in the 90s were basic and basically dealt with security information management (SIM) or security event management (SEM). They were solutions available as tools that had to be deployed on-site in the data center to be protected. This limited scalability, because adding capacity required the purchase of additional equipment.
These early solutions were also built on proprietary databases that forced customers to use technology from a single vendor. If you wanted to move your data to another system, the process was long and complicated. It should also be noted that archiving was more expensive, so only the most valuable data was collected. Furthermore, although the SIM and SEM solutions contained all the data necessary for the defense, the search and alarm were rudimentary. Additionally, they depended on experienced security analysts to research, understand and interpret what they found in the data.
SIEM origins in computer science
As data became more sensitive and technology more powerful, SIEM systems (SIM + SEM) became capable of ingesting, processing and storing a great deal of data. Next-generation SIEM IT solutions are able to use signature-based alerts to identify threats in collected data. However, only those alerts that have identified indicators of compromise (IOC) of a certain threat can be identified in this way.
To be clear, if the type of attack to which a system is subjected has not been cataloged in a series of IOCs, a first generation SIEM is not able to detect it. The main drawback of those systems was the very limited ability to detect unknown cyber threats.
To give a practical example: it was possible to use a rule like this: “give a warning if a user enters 10 consecutive wrong passwords“. In theory this could be used to detect brute force password attacks. But what if the attacker only tried 9 passwords in a row? Or what if the alarm was given for a very forgetful user?
Next Gen SIEM (NGS)
A next generation SIEM is built on a large data platform that provides unlimited scalability and is hosted in the cloud. A next gen SIEM includes log management, advanced threat detection based on behavior analysis and automatic incident response, all on a single platform.
This eliminates the problems that old on-premises systems were prone to. Not having to install anything and being able to send the necessary data to the cloud quite simply, the computing power of the local machine is not compromised and the SIEM can manage all the data safely.
How a SIEM proceeds in cyber threat analysis
1. Data Collection: An IT SIEM solution collects data from across the organization using agents installed on various devices, including endpoints, servers, network equipment and other security solutions. Next generation SIEM includes support for cloud applications and infrastructure, business applications, identity data and non-technical data feeds.
2. Data enrichment: Enrichment adds further context to events. SIEM will enrich data with identity, resources, geolocation and threat information.
3. Data storage: The data will then be stored in a database so that it can be searched for during investigations. The next generation SIEM exploits open source architectures and big data architectures, exploiting their scalability.
4. Correlation and Analysis: SIEM solutions use several techniques to draw actionable conclusions from SIEM data. These techniques vary greatly.
5. Report: A SIEM, particularly a next generation SIEM, gives you the ability to quickly search for data, allowing you to dig through alerts and search for threat actors and indicators of compromise. The displayed data can be saved or exported. It is also possible to use out-of-the-box reports or create ad hoc reports as needed.
What a SIEM is used for
Threat hunting and investigation
The ability to perform threat hunting on a SIEM is critical to understanding the true patterns of attacks based on access, activity and data breaches. By developing a detailed and contextual view of attacks, security analysts can more easily develop policies, countermeasures and incident response processes to help mitigate and remove the threat.
Response in case of an accident
An effective response to incidents is essential to intervene more quickly and reduce the residence time of the threat. For this, a SIEM provides an incident response playbook with configurable automated actions. A SIEM is able to integrate with third party solutions for security orchestration (SOAR) or individual case management.
Defense against insider threats
The reason why insider threats are such a big problem is because it’s not about entering the perimeter, but about exploiting insider positions. They can be your employees, contractors or business associates. It may be they themselves wanting to exploit their location, or their account may have been hacked.
With all kinds of internal threats, the attacker tries to stay hidden, gathering sensitive data to exploit. This could cause significant damage to the company, its position in the industry and its relationship with consumers or investors. By using a SIEM, you avoid this risk.
Cyber threat detection
Your organization is likely to have at least one sensitive data repository. Cybercriminals thrive on looting this data for financial gain. Many breaches begin with a simple phishing email against an organization’s target. Simply clicking on an attachment can leave malicious code behind. A SIEM will allow you to monitor advanced cyberthreat patterns such as phishing, beaconing and lateral movement.
Compliance standards
For many industries, adherence to compliance standards is critical. A SIEM can help by providing reports focused on data compliance requests. Integrated packages covering all major mandates, including PCI DSS, SOX, and ISO 27001, are a standard feature of SIEMs as well.
Next Generation SIEM
A next generation SIEM is not just a cloud hosted system. It also makes use of the implementation of AI and Machine Learning to increase the defense of the IT system.
We will see it in a future article, but it is right to specify that the SOCaaS offered by SOD makes use of the latest generation technology offered by Next Gen. SIEM systems. Contact us to find out more about it and talk to experts who can dispel all your doubts.
[btnsx id=”2931″]
Useful links:
Security: Pentest and verification of vulnerabilities
What is a Network Lateral Movement and how to defend yourself
Is SOCaaS useful for your business?
Computer network security: PT vs. VA

During a cyber attack, hackers have only one goal in mind. This goal could be accessing a developer’s machine and stealing a project’s source code, analyzing emails from a particular executive, or extracting customer data from a server. All they have to do is log into the machine or system that contains the data they want, right? Not exactly. Actually, it’s a little more complicated than that. To achieve their goal, hackers are likely to break into a low-level web server, email account, or employee device, to name a few. From that node, they will move sideways (hence the name network lateral movement) to achieve their goal.
In fact, when attackers compromise a resource on a network, that device is almost never their final destination. In addition, the initial compromise rarely causes serious damage and may go unnoticed. Only if the security teams are able to detect a lateral movement before the attackers reach their intended goal, it is possible to prevent the data breach.
In this article, we will look at some of the more common types of network lateral movement and identify ways in which we can detect the attack and defend ourselves.
Understanding the network lateral movement
Lateral movement occurs when an attacker takes possession of a resource within a network and then extends its reach from that device to others within the same network. Let’s see it with an outline to help us understand better.
The perimeter of the infrastructure to be penetrated is represented with a horizontal line. The upper half represents what is outside the net, while what is below the line represents what is inside. In order for an attacker to enter the network, it must move vertically, ie from the outside to the inside (also called North-South traffic). But once a foothold has been established, it is possible to move sideways or horizontally, ie within the same network (called East-West traffic) to reach the final goal of the attack.
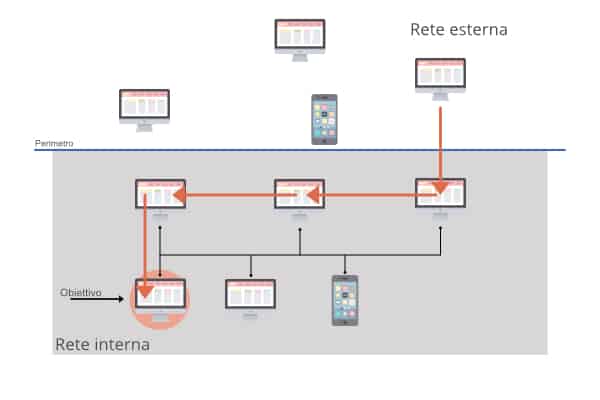
Possible path of a lateral movement. The arrow indicates the network nodes that are involved in the attack.
Approaches to the Lateral Movement
Overall, there are two common methods by which a hacker applies the lateral movement.
First approach: The attacker performs an internal scan to find out what other machines are on the network. In particular, it scans open ports that are listening and machines that suffer from vulnerabilities. At that point, the attacker can abuse these weaknesses to move sideways to another resource.
The second approach to the lateral movement exploits stolen credentials, and is the more common of the two. In this type of attack, the hacker could use an email phishing technique to infect a machine that interfaces with a particular server. Then he can use his login to recover passwords via a keylogger or other similar tools. At this point, he can use whatever credentials he was able to obtain to impersonate the user who was the victim of the phishing and log in to another machine. Once you have established access to that computer, you can repeat the tactic looking for additional credentials and / or privileges to exploit. In this way, the attacker can make their way and create remote connections to the target device.
In both cases it is difficult to identify the attack, because it does not occur through software or application malfunctions.
How to defend yourself
A lateral movement often manifests itself through anomalous network activity. For example, it is suspicious that a machine, which normally communicates with a few others, starts scanning the entire network. The same is true if that machine tries to connect to open ports, to interact with services and credentials with which it normally has no contact, or to use a username that has never been used before.
The list of alarm bells goes on and on. The key thing to understand is that a lateral movement involves machines doing something out of their routine, without proper authorization from IT.
This is what gives organizations the ability to detect this type of attack. Implementing log file monitoring is a first step in defense. Ideally, the data should be constantly analyzed for anomalies and possible breaches.
Defense issues
These defenses are not infallible. Security teams that simply rely on log files limit the scope of their defensive position, for example, due to log files collected only from particular applications. You might decide to monitor a certain service for credential theft, but attackers might not use that particular service to perform a lateral movement. This means that any malicious actions that do not use the monitored services will not be detected promptly.
In addition to this, hackers know the types of protocols that security personnel tend to monitor, making their task even more complex. Attackers can use this knowledge to model their attack campaigns in order to have a better chance of going unnoticed. It is one of the reasons why the MITER ATT & CK database was created to collect known techniques and raise the defenses.
The advantage of a SOCaaS
It is not enough for organizations to seek lateral movement using log files or an EDR tool. It is necessary to turn attention to the network as a whole. In this way it is possible to see all network traffic, establish a baseline of normal network activity for each user and device, and then monitor any unusual actions that could be indicative of attacks. It is known as anomaly detection, and is more comprehensive and often easier than examining each log file for out-of-the-ordinary events.
The problem with anomaly detection is that many of these irregularities are benign, and a lot of time is spent analyzing them. What is needed to separate harmful lateral movement from benign network anomalies is an understanding of the aspect of harmful behavior.
This is where a complete system that uses both behavioral analysis tools and professional security technicians comes into play.
The SOCaaS offered by SOD includes a Security Data Lake (SDL) for data collection and various tools for data analysis. One of these is the UEBA, particularly suitable for the detection of social threats, as it analyzes user behavior through AI using their actions as a source of data.
With these and other tools that make up the SOC, you can actively reduce the risk of attacks on your corporate data. If you are interested in learning more about SOD SOCaaS, I invite you to visit the dedicated page or contact us directly.
[btnsx id=”2931″]
Useful links:
Is SOCaaS useful for your business
Computer Network Security: PT vs. VA
Cyber Security: Pentest and verification of vulnerabilities
Customers
Twitter FEED
Recent activity
-
SecureOnlineDesktop
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes L'impatto crescente delle minacce informatiche, su sistemi operativi privati op… https://t.co/FimxTS4o9G
-
SecureOnlineDesktop
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes The growing impact of cyber threats, on private or corporate operating systems… https://t.co/y6G6RYA9n1
-
SecureOnlineDesktop
Tempo di lettura stimato: 6 minuti Today we are talking about the CTI update of our services. Data security is… https://t.co/YAZkn7iFqa
-
SecureOnlineDesktop
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes Il tema della sicurezza delle informazioni è di grande attualità in questo peri… https://t.co/tfve5Kzr09
-
SecureOnlineDesktop
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes The issue of information security is very topical in this historical period ch… https://t.co/TP8gvdRcrF
Newsletter
{subscription_form_1}© 2023 Secure Online Desktop s.r.l. All Rights Reserved. Registered Office: via dell'Annunciata 27 – 20121 Milan (MI), Operational Office: via statuto 3 - 42121 Reggio Emilia (RE) – PEC [email protected] Tax code and VAT number 07485920966 – R.E.A. MI-1962358 Privacy Policy - ISO Certifications