Estimated reading time: 5 minutes
Just like any other IT field, the cybersecurity market is driven by hype . Currently hype towards XDR, ie eXtended Detection and Response .
XDR is the latest in threat detection and response, a key element of a company’s infrastructure and data defense .
What exactly is XDR?
XDR is an alternative to traditional responsive approaches that only provide layer visibility on attacks . I refer to procedures such as detection and endpoint response (EDR), network traffic analysis (NTA) and SIEM , which we have talked about in many other articles.
The layer visibility implies that various services are adopted, stratified (layers), which each keep under control a specific entity in the infrastructure. This can be problematic. In fact, you need to make sure that layers don’t end up isolated, making it difficult, or nearly impossible to manage and view data. layer visibility provides important information, but can also lead to problems, including :
Collecting too many incomplete and contextless alerts. EDR detects only 26% of initial attack vectors and due to the high volume of security alerts, 54% of professionals security ignores warnings that should be investigated .
Complex and time-consuming investigations requiring specialist expertise . With EDR, the median time to identify a breach has increased to 197 days, and the median time to contain a breach has increased to 69 days.
Tools focused on technology rather than user or business . EDR focuses on technology gaps rather than the operational needs of users and companies. With more than 40 tools used in an average Security Operations Center (SOC), 23% of security teams spend their time maintaining and managing security tools rather than investigating . ( Source )

For already overloaded security teams, the result can be an endless stream of events , too many tools and information to switch between, longer time frames for detection and security expenses that are beyond budget and are not even fully effective .
What’s new in eXtended Detection Response
XDR implements a proactive approach to threat detection and response . It offers visibility into data across networks, clouds and endpoints, while applying analytics and automation to address today’s increasingly sophisticated threats. The benefits of the XDR approach for security teams are manifold:
Identify hidden, stealth and sophisticated threats proactively and quickly.
Track threats across any source or location within your organization. < br> Increase the productivity of people working with technology.
Get more from their security investments .
Conclude investigations in a way more efficient .
From a business perspective, XDR enables companies to detect cyber threats and stop attacks, as well as simplify and strengthen security processes. As a result, it enables companies to better serve users and accelerate digital transformation initiatives. When users, data and applications are protected, companies can focus on strategic priorities.
Why consider it for your company
The two main reasons why this approach is beneficial are: endpoints do not have visibility into threats in places like cloud services , and it may not be possible to put a < em> software agent on all company endpoints .
But there are other reasons to consider too. The addition of other data sources can provide more context in the EDR results, improving triage and investigation of alerts . Providers are moving not only to provide more and better organized data, but also by delivering analytics platforms to lighten the analytical load on operators. This translates into ease of use and reduced operating costs.
XDR can seem very attractive as a product: Tight integration of parts, highly tuned content (as the provider has total control over the events from the data sources), use of analytics and response automation.

What to pay attention to before adoption
Some providers are positioning their XDR as the ultimate threat detection solution . However, many vendors are unable to offer all the tools needed to get the advantage sold. Some providers offer endpoint and cloud monitoring in the package, others endpoint and network monitoring, but when looking at the comprehensive needs of most organizations, there are often missing details in the overall picture.
And if, once the company engages with a provider and notices a lack in one of the monitored sectors, what are the possible solutions? A situation of vendor lock-in from which to break free means to sever a contract and then open another one, with all the consequent costs.
XDR as an approach, not as a product
Before entering into a contract with a provider that sells a solution as final, it is always good to weigh the benefits and implications analytically.
Tight, two-way integration of multiple threat detection and response capabilities is the first distinguishing feature. But it is not necessary to buy two technology components from the same vendor to achieve good integration. Indeed, many products have the ability to integrate with some solutions from other vendors as one of their main strengths.
The XDR approach must provide a platform that allows the necessary data collection and storage , but also strong analytical skills, to orchestrate and automate response actions provided by the other parts of the solution. A cloud based Next Generation SIEM is a perfect solution.
How to move then?
The interest in XDR products is a clear signal that excessive fragmentation was leading to excessive complexity. A little consolidation is good, but it must be done while protecting flexibility and the ability to follow the best solutions.
In our opinion, a SOCaaS is an optimal solution. Provides next generation SIEM , with strong analytical capabilities. In addition, it also integrates artificial intelligence that helps in time to recognize threats through behavior analysis. A SOCaaS is the future of security operating platforms.
To find out with our services they can help you protect the data of your company and your customers, contact us, we will gladly answer all your questions.
Useful links:

Estimated reading time: 6 minutes
I dati di threat intelligence forniscono alle aziende approfondimenti rilevanti e tempestivi necessari per comprendere, prevedere, rilevare e rispondere alle minacce alla sicurezza informatica. Le soluzioni di intelligence sulle minacce raccolgono, filtrano e analizzano grandi volumi di dati grezzi relativi a fonti esistenti o emergenti di minacce. Il risultato sono feed di threat intelligence e rapporti di gestione. I data scientist e i team di sicurezza utilizzano questi feed e report per sviluppare un programma con risposte mirate agli incidenti per attacchi specifici.
Tutti, dalla prevenzione delle frodi alle operazioni di sicurezza all’analisi dei rischi, traggono vantaggio dalla threat intelligence. Il software di intelligence sulle minacce fornisce visualizzazioni interattive e in tempo reale dei dati relativi alle minacce e alle vulnerabilità.
Il vantaggio offerto agli analisti ed esperti di sicurezza è evidente e serve a identificare facilmente e rapidamente i modelli degli attori delle minacce. Comprendere la fonte e l’obiettivo degli attacchi aiuta i capi d’azienda a mettere in atto difese efficaci per mitigare i rischi e proteggersi dalle attività che potrebbero avere un impatto negativo sull’azienda.
La cyber threat intelligence può essere classificata come strategica, tattica oppure operativa. Quella Strategica riguarda le capacità e gli intenti generali degli attacchi informatici. Di conseguenza anche lo sviluppo di strategie informate associate alla lotta contro le minacce a lungo termine. Quella Tattica riguarda le tecniche e le procedure che gli aggressori potrebbero utilizzare nelle operazioni quotidiane. Infine, la threat intelligence Operativa, fornisce informazioni altamente tecniche a livello forense riguardanti una specifica campagna di attacco.

Il ciclo della threat intelligence
Le soluzioni di intelligence sulle minacce raccolgono dati grezzi sugli attori e le minacce da varie fonti. Questi dati vengono poi analizzati e filtrati per produrre feed e rapporti di gestione che contengono informazioni che possono essere utilizzate in soluzioni automatizzate di controllo della sicurezza. Lo scopo principale di questo tipo di sicurezza è quello di mantenere le organizzazioni informate sui rischi delle minacce persistenti avanzate, delle minacce zero-day e degli exploit, e su come proteggersi da esse.
Il ciclo di intelligence delle minacce informatiche consiste nelle seguenti fasi.
Pianificazione: I requisiti dei dati devono essere prima definiti.
Raccolta: Si raccolgono grandi quantità di dati grezzi da fonti interne ed esterne di threat intelligence.
Elaborazione: I dati grezzi sono filtrati, categorizzati e organizzati.
Analisi: Questo processo trasforma i dati grezzi in flussi di informazioni sulle minacce con l’uso di tecniche analitiche strutturate in tempo reale e aiuta gli analisti a individuare gli indicatori di compromissione (IOC).
Diffusione: I risultati dell’analisi vengono immediatamente condivisi con i professionisti della sicurezza informatica e gli analisti di threat intelligence.
Feedback: Se tutte le domande trovano risposta, il ciclo si conclude. Se ci sono nuovi requisiti, il ciclo ricomincia dalla fase di pianificazione.
Indicatori comuni di compromissione
Le aziende sono sempre più sotto pressione per gestire le vulnerabilità della sicurezza e il panorama delle minacce è in continua evoluzione. I feed di threat intelligence possono aiutare in questo processo identificando gli indicatori comuni di compromissione (IOC). Non solo, possono anche raccomandare i passi necessari per prevenire attacchi e infezioni. Alcuni degli indicatori di compromissione più comuni includono:
Indirizzi IP, URL e nomi di dominio: Un esempio potrebbe essere un malware che prende di mira un host interno che sta comunicando con un noto attore di minacce.
Indirizzi e-mail, oggetto delle e-mail, link e allegati: Un esempio potrebbe essere un tentativo di phishing che si basa su un utente ignaro che clicca su un link o un allegato e avvia un comando dannoso.
Chiavi di registro, nomi di file e hash di file e DLL: Un esempio potrebbe essere un attacco da un host esterno che è già stato segnalato per un comportamento nefasto o che è già infetto.

Quali strumenti per la threat intelligence
Il crescente aumento del malware e delle minacce informatiche ha portato a un’abbondanza di strumenti di threat intelligence che forniscono preziose informazioni per proteggere le aziende.
Questi strumenti si presentano sotto forma di piattaforme sia open source che proprietarie. Queste forniscono una serie di capacità di difesa contro le minacce informatiche, come l’analisi automatizzata dei rischi, la raccolta di dati privati, strumenti di ricerca rapida di threat intelligence, la segnalazione e condivisione di queste informazioni tra più utenti, avvisi curati, analisi dei rischi di vulnerabilità, monitoraggio del dark web, mitigazione automatizzata dei rischi, threat hunting e molto altro.
Abbiamo parlato di uno di questi strumenti in un altro articolo: il Mitre Att&ck. Questo è uno strumento molto utile per conoscere i comportamenti e le tecniche di attacco hacker. Questo grazie alle informazioni raccolte dalla threat intelligence e la conseguente condivisione. Un framework come questo è molto efficiente per creare meccanismi difensivi che consentono di mettere in sicurezza le infrastrutture aziendali.
Intelligenza artificiale e informazioni sulle minacce
Come abbiamo visto prima, la raccolta di informazioni da varie fonti non è altro che una delle fasi. Queste devono poi venire analizzate e successivamente elaborate in protocolli di controllo, per essere davvero utili per la sicurezza.
Per questo tipo di lavori di analisi, definizione di comportamenti baseline e controllo dei dati ci si affida sempre di più all’intelligenza artificiale e al deep learning. Un Next Generation SIEM, affiancato a una soluzione UEBA sono perfetti per questo tipo di protezione.
Il controllo del comportamento delle entità all’interno del perimetro effettuato dal UEBA è in grado di identificare ogni comportamento sospetto, in base alle informazioni raccolte e analizzate dal SIEM.
Conclusioni
Gli strumenti di difesa che abbiamo nominato sono il valore primario di un piano di sicurezza aziendale. Adottare soluzioni specifiche, implementare la threat intelligence e quindi una ricerca attiva degli indicatori di minacce, offre una posizione di vantaggio strategica. L’azienda può operare un passo avanti ai criminali, i quali possono far leva solo sull’effetto sorpresa contro le loro vittime. Proprio per questa situazione generale, ogni azienda dovrebbe essere nelle condizioni di non farsi cogliere alla sprovvista. Implementare soluzioni proattive è ormai necessario.
La threat intelligence è quindi un’arma da difesa dietro la quale mettere al riparo le risorse più importanti per poter lavorare in tranquillità.
Se vuoi sapere come possiamo aiutarti con i nostri servizi dedicati alla sicurezza, non esitare a contattarci, saremo lieti di rispondere a ogni domanda.
Useful links:
Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) – maggiore efficacia per la sicurezza IT
Progetti di Secure Online Desktop
Cos’è la Cyber Security? Definizione e proposte
Prevenire il shoulder surfing e il furto di credenziali aziendali

Estimated reading time: 5 minutes
In the previous article we have seen the most common use cases of a SOCaaS , explaining how it can be useful for companies to use this tool to prevent cyber attacks and also explaining which are the most common Threat Models .
In this article, however, we will take a closer look at some of the more common indicators of compromise (IOC). First we will briefly look at the malware threat models that the use of a SOCaaS can prevent and block. As it works, a SOCaaS can be very flexible and analyze a lot of data at the same time, thus providing in-depth and accurate results.

Malware Threat Models
It is important to know how to distinguish and classify the different types of malware to understand how they can infect systems and devices, the level of threat they represent and how to protect against them. We at SOD recommend adopting the use of a SOCaaS in order to be able to classify the entire range of malware or potentially unwanted objects. Malware is categorized based on the activity they perform on infected systems.
Wannacry Malware Detection
Thanks to this threat model it is possible to detect the behavior of the well-known malware Wannacry.
Wannacry malware is a ransomware that attacks the system by encrypting files of particular importance to an organization in order to make them illegible.
Early detection of ransomware is probably the most effective action you can take to defend yourself. There are also services that are able to block the action of the malware and restore any files already encrypted with those of a backup, for example Acronis Cyber Protect Cloud .
Network anomaly followed by data infiltration
Identifies successful network data aggregation attempts, followed by signs of data infiltration. Below we see some of the anomalies and how the use of a SOCaaS can identify important clues to counter threats.
During a network scan you may notice enumerations of AD accounts and privileges, count of LDAP services outside the corporate network and a suspicious number of ticket requests to Kerberos protocol . In addition, other indicators can be a spike in LDAP traffic and the enumeration of SMB services.
As regards the anomalies of the network drive , the use of a SOCaaS is able to control access to the sharepoint in order to identify an unusual number of accesses to shared elements. This also in relation to users and their level of access.
In terms of Data Aggregation and data infiltration, the quantity of bytes downloaded from the server ports and via FTP protocols are monitored, as well as an unusual quantity of bytes transmitted to the external.
Petrwrap / Goldeneye / Amalware detection
This threat model aims to detect malware Petrwrap . The use of a SOCaaS can detect network scanning activity by monitoring the number of SMBv1 activities, as well as anomalies in these activities. Attempting to reach a never-before-reached host may also be an indicator.
Another way in which these threats can be detected with the use of SOCaaS is by auditing of suspicious privileged activity. For example, it is verified that there is no escaletion of privileges, unusual access to an admin zone or even tampering with log files.
Risk indicators in general
Risk indicators are metrics used to show that the organization is subject to or has a high probability of being subject to a risk.
These indicators are used to classify the type of behavior or threat for a policy and can be used in multiple policies for different functionality based on the data source. Risk indicators can be chained with threat models to identify sophisticated attacks across multiple data sources.
In essence, these are clues or alarm bells that indicate events that a company’s security operators should pay particular attention to. The use of a SOCaaS can help identify these clues by analyzing large amounts of data and logs in a short time.
Below is a non-exhaustive list of some of the most common threat indicators that are identifiable through the use of a SOCaaS. We will divide them into different areas, for clarity.
As for accounts, obviously, blocking an account is an alarm bell, as well as an unusual number of accounts created or a disproportionate number of failed authentication. Finally, the use of a SOCaaS could indicate an IOC as a suspicious number of accounts running concurrently .
Access
The anomalies concerning the access or in any case the account include the detection of access to the anomalous administrative sherepoint but also the loading times of the anomalous applications. Applications that use an unusual amount of memory may also be indicators of compromise.
As for accounts, obviously, blocking an account is an alarm bell, as well as an unusual number of accounts created or a disproportionate number of failed authentication. Finally, the use of a SOCaaS could indicate an IOC as a suspicious number of accounts running concurrently .

Networks
Network alarm bells are, of course, the most common. Since networks are like “roads” of a corporate infrastructure, it is normal that anomalous behaviors in these are particularly relevant.
Common indicators are abnormal DNS zone transfers or failed requests to the firewall. But also an abnormal number of running hosts or ICMP connections. Traffic in general is also controlled through the use of SOCaaS, so that any suspicious data movement is analyzed or otherwise verified. Examples of this are packet movements to critical ports, RDP, SSH, or connection attempts to a DHCP server. These events often indicate abnormal attempts to connect to objects or network shares.
Through the use of a SOCaaS it is also very simple to control the behavior of the accounts that often show alarm bells in themselves . For example, an account logging into a host for the first time, creating an account, or adding privileges.
Conclusions
Relying on luck to catch threats is madness , as demonstrated by SolarWinds attack .
Create your luck with our SOCaaS solution , making sure you spot threats before incidents happen and that you are “lucky” enough to counter them.
Contact us to find out how our services can strengthen your company’s defenses, we will be happy to answer any questions.
Useful links:




A legitimate question that often arises is whether the Penetration Test is necessary for compliance with the ISO 27001 standard. To fully understand the answer, it is necessary to clarify what is meant by these terms and to understand the relationship between all the components of the certification.
ISO 27001 standard
A technical standard, also incorrectly called a standard, is a document that describes the specifications that a certain object / body / entity must comply with in order to be certified. In general, a standard describes the requirements of materials, products, services, activities, processes, terminology, methodologies and other aspects concerning the subject of the standard. In very simple words, norms are rules that regulate almost everything by offering constructive and methodological standards.
The ISO 27001 standard (ISO / IEC 27001: 2013) is the international standard that describes the best practices for an ISMS, Information Security Management System. Although following the standard is not mandatory, it is necessary to obtain a certification to guarantee logical, physical and organizational security.
Obtaining an ISO 27001 certification demonstrates that your company is following information security best practices and provides independent and qualified control. Safety is guaranteed to be in line with the international standard and company objectives.
Of great importance for the ISO 27001 standard is Annex A “Control objective and controls”, which contains the 133 controls that the company concerned must comply with.
Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Test
When performing a Vulnerability Assessment on the network and computer systems, the aim is to identify all technical vulnerabilities present in operating systems and software. Some examples of vulnerabilities can be SQL Injection, XSS, CSRF, weak passwords, etc. The vulnerability detection indicates that there is a recognized security risk due to a problem of some kind. It does not say whether or not it is possible to exploit the vulnerability. To find out, it is necessary to carry out a Penetration Test (or pentest).
To explain the above, imagine that you have a web application that is vulnerable to SQL Injection which could allow an attacker to perform operations on the database. A VA identifies this vulnerability, ie it may be possible to access the database. Following the vulnerability assessment, if a pentest is performed and the vulnerability can be exploited, the risk would be demonstrated.
To comply with control A.12.6.1 of Annex A of the ISO 27001 standard, it is necessary to prevent the exploitation of technical vulnerabilities. However, the decision on how to proceed is up to you. Is it therefore necessary to perform a Pentest? Not necessarily.
After the vulnerability analysis, we could fix and fix the weaknesses and eliminate the risk before performing a pentest. Therefore, for the purposes of compliance with the ISO 27001 standard, the required result can be obtained simply by performing the vulnerability assessment and solving the potential problems that have arisen.
Having said that, we strongly recommend that you carry out a complete Penetration Test to be really sure of compliance with the standard. It can help you prioritize problems and tell you how vulnerable your systems are.
Contact professionals
Esistono sul mercato diverse soluzioni per svolgere pentest. Sono software che possono agevolare il lavoro e facilitare il test, ma se azionati da personale inesperto, possono anche creare dei problemi. e’ possibile che la rete ne risulti rallentata e i computer sensibilmente meno reattivi, fino anche a possibili crash di uno o piu’ dei sistemi coinvolti.
Puntando alla certificazione per lo standard ISO 27001, e’ meglio non fare gli eroi e assicurarsi davvero che i controlli siano rispettati. Richiedere l’intervento di professionisti del settore, serve proprio a minimizzare i rischi e assicurarsi che il processo sia svolto in modo impeccabile.
SOD offre un servizio di verifica delle vulnerabilita’ e pentest affidandosi ad hacker etici professionisti. Dopo un primo colloquio, le varie fasi del processo sono eseguite per verificare e testare le potenziali minacce. E’ possibile anche richiedere che la verifica delle vulnerabilita’ sia svolta con regolarita’ per verificare la sicurezza dei sistemi.
Richiedi informazioni specifiche, oppure visita la pagina dedicata. Per ulteriori informazioni sulle nostre certificazioni, e’ possibile visitare l’apposita pagina.
There are several solutions on the market to perform pentest. They are software that can facilitate the work and facilitate the test, but if operated by inexperienced personnel, they can also create problems. it is possible that the network will be slowed down and the computers noticeably less reactive, up to possible crashes of one or more of the systems involved.
Aiming for ISO 27001 certification, it’s best not to be heroes and really make sure the controls are respected. Requesting the intervention of professionals in the sector serves precisely to minimize risks and make sure that the process is carried out flawlessly.
SOD offers a vulnerability verification and pentest service relying on professional ethical hackers. After an initial interview, the various stages of the process are carried out to verify and test potential threats. It is also possible to request that the verification of vulnerabilities be carried out regularly to verify the security of the systems.
Request specific information, or visit the dedicated page. For more information on our certifications, you can visit the appropriate page.
[btnsx id=”2931″]
Useful links:
Security: pentest and verification of vulnerabilities

A SIEM solution in IT is one of the essential components of a SOC (Security Operation Center). Its task is to collect information and analyze it in search of anomalies and possible breaches in the system. But the defense process hasn’t always been that simple. What we now call SIEM, Security Information and Event Management, is the union of two different types of cyber security tools.
SIM and SEM: the origins
Before the arrival of a complete SIEM solution in computing, security was heavily focused on perimeter security and did not keep the internal network adequately controlled. The first solutions developed in the 90s were basic and basically dealt with security information management (SIM) or security event management (SEM). They were solutions available as tools that had to be deployed on-site in the data center to be protected. This limited scalability, because adding capacity required the purchase of additional equipment.
These early solutions were also built on proprietary databases that forced customers to use technology from a single vendor. If you wanted to move your data to another system, the process was long and complicated. It should also be noted that archiving was more expensive, so only the most valuable data was collected. Furthermore, although the SIM and SEM solutions contained all the data necessary for the defense, the search and alarm were rudimentary. Additionally, they depended on experienced security analysts to research, understand and interpret what they found in the data.
SIEM origins in computer science
As data became more sensitive and technology more powerful, SIEM systems (SIM + SEM) became capable of ingesting, processing and storing a great deal of data. Next-generation SIEM IT solutions are able to use signature-based alerts to identify threats in collected data. However, only those alerts that have identified indicators of compromise (IOC) of a certain threat can be identified in this way.
To be clear, if the type of attack to which a system is subjected has not been cataloged in a series of IOCs, a first generation SIEM is not able to detect it. The main drawback of those systems was the very limited ability to detect unknown cyber threats.
To give a practical example: it was possible to use a rule like this: “give a warning if a user enters 10 consecutive wrong passwords“. In theory this could be used to detect brute force password attacks. But what if the attacker only tried 9 passwords in a row? Or what if the alarm was given for a very forgetful user?
Next Gen SIEM (NGS)
A next generation SIEM is built on a large data platform that provides unlimited scalability and is hosted in the cloud. A next gen SIEM includes log management, advanced threat detection based on behavior analysis and automatic incident response, all on a single platform.
This eliminates the problems that old on-premises systems were prone to. Not having to install anything and being able to send the necessary data to the cloud quite simply, the computing power of the local machine is not compromised and the SIEM can manage all the data safely.
How a SIEM proceeds in cyber threat analysis
1. Data Collection: An IT SIEM solution collects data from across the organization using agents installed on various devices, including endpoints, servers, network equipment and other security solutions. Next generation SIEM includes support for cloud applications and infrastructure, business applications, identity data and non-technical data feeds.
2. Data enrichment: Enrichment adds further context to events. SIEM will enrich data with identity, resources, geolocation and threat information.
3. Data storage: The data will then be stored in a database so that it can be searched for during investigations. The next generation SIEM exploits open source architectures and big data architectures, exploiting their scalability.
4. Correlation and Analysis: SIEM solutions use several techniques to draw actionable conclusions from SIEM data. These techniques vary greatly.
5. Report: A SIEM, particularly a next generation SIEM, gives you the ability to quickly search for data, allowing you to dig through alerts and search for threat actors and indicators of compromise. The displayed data can be saved or exported. It is also possible to use out-of-the-box reports or create ad hoc reports as needed.
What a SIEM is used for
Threat hunting and investigation
The ability to perform threat hunting on a SIEM is critical to understanding the true patterns of attacks based on access, activity and data breaches. By developing a detailed and contextual view of attacks, security analysts can more easily develop policies, countermeasures and incident response processes to help mitigate and remove the threat.
Response in case of an accident
An effective response to incidents is essential to intervene more quickly and reduce the residence time of the threat. For this, a SIEM provides an incident response playbook with configurable automated actions. A SIEM is able to integrate with third party solutions for security orchestration (SOAR) or individual case management.
Defense against insider threats
The reason why insider threats are such a big problem is because it’s not about entering the perimeter, but about exploiting insider positions. They can be your employees, contractors or business associates. It may be they themselves wanting to exploit their location, or their account may have been hacked.
With all kinds of internal threats, the attacker tries to stay hidden, gathering sensitive data to exploit. This could cause significant damage to the company, its position in the industry and its relationship with consumers or investors. By using a SIEM, you avoid this risk.
Cyber threat detection
Your organization is likely to have at least one sensitive data repository. Cybercriminals thrive on looting this data for financial gain. Many breaches begin with a simple phishing email against an organization’s target. Simply clicking on an attachment can leave malicious code behind. A SIEM will allow you to monitor advanced cyberthreat patterns such as phishing, beaconing and lateral movement.
Compliance standards
For many industries, adherence to compliance standards is critical. A SIEM can help by providing reports focused on data compliance requests. Integrated packages covering all major mandates, including PCI DSS, SOX, and ISO 27001, are a standard feature of SIEMs as well.
Next Generation SIEM
A next generation SIEM is not just a cloud hosted system. It also makes use of the implementation of AI and Machine Learning to increase the defense of the IT system.
We will see it in a future article, but it is right to specify that the SOCaaS offered by SOD makes use of the latest generation technology offered by Next Gen. SIEM systems. Contact us to find out more about it and talk to experts who can dispel all your doubts.
[btnsx id=”2931″]
Useful links:
Security: Pentest and verification of vulnerabilities
What is a Network Lateral Movement and how to defend yourself
Is SOCaaS useful for your business?
Computer network security: PT vs. VA

During a cyber attack, hackers have only one goal in mind. This goal could be accessing a developer’s machine and stealing a project’s source code, analyzing emails from a particular executive, or extracting customer data from a server. All they have to do is log into the machine or system that contains the data they want, right? Not exactly. Actually, it’s a little more complicated than that. To achieve their goal, hackers are likely to break into a low-level web server, email account, or employee device, to name a few. From that node, they will move sideways (hence the name network lateral movement) to achieve their goal.
In fact, when attackers compromise a resource on a network, that device is almost never their final destination. In addition, the initial compromise rarely causes serious damage and may go unnoticed. Only if the security teams are able to detect a lateral movement before the attackers reach their intended goal, it is possible to prevent the data breach.
In this article, we will look at some of the more common types of network lateral movement and identify ways in which we can detect the attack and defend ourselves.
Understanding the network lateral movement
Lateral movement occurs when an attacker takes possession of a resource within a network and then extends its reach from that device to others within the same network. Let’s see it with an outline to help us understand better.
The perimeter of the infrastructure to be penetrated is represented with a horizontal line. The upper half represents what is outside the net, while what is below the line represents what is inside. In order for an attacker to enter the network, it must move vertically, ie from the outside to the inside (also called North-South traffic). But once a foothold has been established, it is possible to move sideways or horizontally, ie within the same network (called East-West traffic) to reach the final goal of the attack.
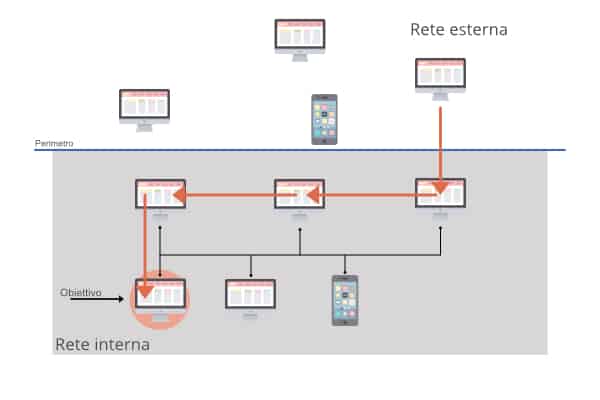
Possible path of a lateral movement. The arrow indicates the network nodes that are involved in the attack.
Approaches to the Lateral Movement
Overall, there are two common methods by which a hacker applies the lateral movement.
First approach: The attacker performs an internal scan to find out what other machines are on the network. In particular, it scans open ports that are listening and machines that suffer from vulnerabilities. At that point, the attacker can abuse these weaknesses to move sideways to another resource.
The second approach to the lateral movement exploits stolen credentials, and is the more common of the two. In this type of attack, the hacker could use an email phishing technique to infect a machine that interfaces with a particular server. Then he can use his login to recover passwords via a keylogger or other similar tools. At this point, he can use whatever credentials he was able to obtain to impersonate the user who was the victim of the phishing and log in to another machine. Once you have established access to that computer, you can repeat the tactic looking for additional credentials and / or privileges to exploit. In this way, the attacker can make their way and create remote connections to the target device.
In both cases it is difficult to identify the attack, because it does not occur through software or application malfunctions.
How to defend yourself
A lateral movement often manifests itself through anomalous network activity. For example, it is suspicious that a machine, which normally communicates with a few others, starts scanning the entire network. The same is true if that machine tries to connect to open ports, to interact with services and credentials with which it normally has no contact, or to use a username that has never been used before.
The list of alarm bells goes on and on. The key thing to understand is that a lateral movement involves machines doing something out of their routine, without proper authorization from IT.
This is what gives organizations the ability to detect this type of attack. Implementing log file monitoring is a first step in defense. Ideally, the data should be constantly analyzed for anomalies and possible breaches.
Defense issues
These defenses are not infallible. Security teams that simply rely on log files limit the scope of their defensive position, for example, due to log files collected only from particular applications. You might decide to monitor a certain service for credential theft, but attackers might not use that particular service to perform a lateral movement. This means that any malicious actions that do not use the monitored services will not be detected promptly.
In addition to this, hackers know the types of protocols that security personnel tend to monitor, making their task even more complex. Attackers can use this knowledge to model their attack campaigns in order to have a better chance of going unnoticed. It is one of the reasons why the MITER ATT & CK database was created to collect known techniques and raise the defenses.
The advantage of a SOCaaS
It is not enough for organizations to seek lateral movement using log files or an EDR tool. It is necessary to turn attention to the network as a whole. In this way it is possible to see all network traffic, establish a baseline of normal network activity for each user and device, and then monitor any unusual actions that could be indicative of attacks. It is known as anomaly detection, and is more comprehensive and often easier than examining each log file for out-of-the-ordinary events.
The problem with anomaly detection is that many of these irregularities are benign, and a lot of time is spent analyzing them. What is needed to separate harmful lateral movement from benign network anomalies is an understanding of the aspect of harmful behavior.
This is where a complete system that uses both behavioral analysis tools and professional security technicians comes into play.
The SOCaaS offered by SOD includes a Security Data Lake (SDL) for data collection and various tools for data analysis. One of these is the UEBA, particularly suitable for the detection of social threats, as it analyzes user behavior through AI using their actions as a source of data.
With these and other tools that make up the SOC, you can actively reduce the risk of attacks on your corporate data. If you are interested in learning more about SOD SOCaaS, I invite you to visit the dedicated page or contact us directly.
[btnsx id=”2931″]
Useful links:
Is SOCaaS useful for your business
Computer Network Security: PT vs. VA
Cyber Security: Pentest and verification of vulnerabilities

Mitre Att&ck is a global knowledge base of adversary tactics and techniques based on real observations of cyber attacks. These are displayed in arrays organized by attack tactics, from initial system access and data theft to machine control. There are arrays for common desktop platforms (Linux, macOS and Windows) and for mobile ones.
What is MITRE ATT&CK ™ and what does it mean?
ATT&CK stands for “adversarial tactics, techniques, and common knowledge” and that is: tactics, adversary techniques and common knowledge. Let’s try to go deeper.
Tactics and techniques are a modern way of thinking about cyber attacks. Rather than looking at the results of an attack – an indicator of compromise (IoC) – security analysts should look at the tactics and techniques that indicate an attack is in progress. Tactics represent the goal you want to achieve, while techniques represent how an opponent plans to achieve it.
Common knowledge is the documented use of tactics and techniques used by opponents. Essentially, common knowledge is the documentation of the procedures used by the attacker. Those familiar with cybersecurity may be familiar with the term “tactics, techniques and procedures” or TTP. This same concept has been used by ATT&CK ™, replacing the term procedure with common knowledge.
Who is MITRE and what is the goal of ATT&CK ™?
MITRE is a US government funded research organization based in Bedford, MA, and McLean, VA. The company was spun off from MIT in 1958 and was involved in a number of top secret commercial projects for various agencies. These included the development of the FAA’s air traffic control system and the AWACS radar system. MITRE has a substantial cybersecurity practice funded by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
A curiosity: the word Mitre means nothing. Apparently one of the first members, James McCormack, wanted a name that meant nothing but was evocative. Some mistakenly think it means Massachusetts Institute of Technology Research and Engineering.
ATT&CK’s goal is to create a comprehensive list of known opponent tactics and techniques used during a cyber attack. Open to governmental, educational and commercial organizations, it should be able to gather a wide, and hopefully comprehensive, range of attack phases and sequences. MITRE ATT&CK aims to create a standard taxonomy to make communications between organizations more specific.
How is the ATT&CK ™ matrix used?
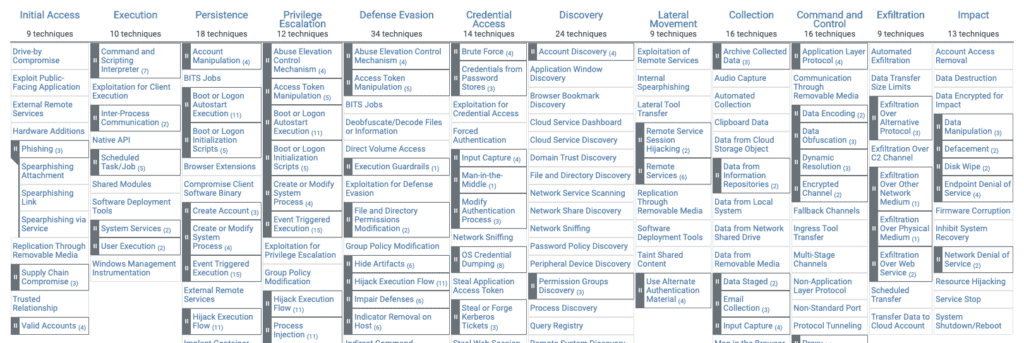
The matrix visually organizes all known tactics and techniques in an easy to understand format. Attack tactics are shown above, and individual techniques are listed below in each column. An attack sequence would involve at least one technique per tactic, and a complete attack sequence would be constructed by moving from left (Initial Access) to right (Command and Control). It is possible to use more techniques for a single tactic. For example, an attacker might try both a Spearphishing Attachment and a Spearphishing Link as initial login tactics.
Here is an example of a matrix:
In this matrix there are all the phases of an attack sequence. It is organized so that the tactics are ordered from right to left according to the attack sequence. Under each tactic the corresponding techniques, some of which contain sub-techniques. The two techniques mentioned above are actually sub-techniques of phishing which are part of the first step in the sequence (first column on the left).
Example
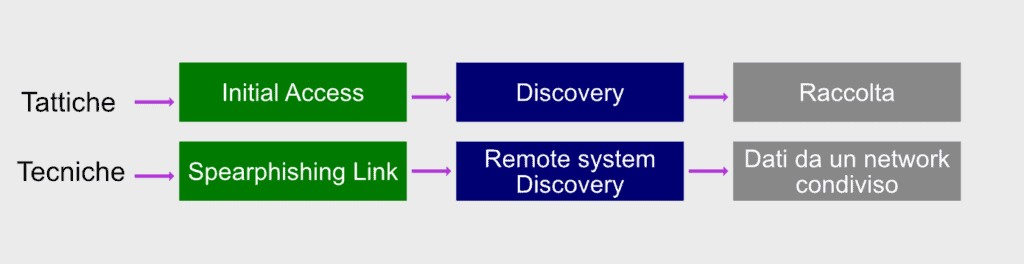
It is not necessary for an attacker to use all eleven tactics at the top of the matrix. Rather, the attacker will use the minimum number of tactics to achieve his goal, as it is more efficient and provides less chance of discovery. In this attack (illustrated in the diagram below), the adversary performs initial access to the CEO’s administrative assistant credentials using a Spearphishing link delivered in an email. Once in possession of the administrator’s credentials, the attacker searches for a Remote System Discovery of the Discovery phase.
Let’s say they’re looking for sensitive data in a Dropbox folder that the admin also has access to, so there’s no need to increase privileges. The collection, which is the last stage, is done by downloading the files from Dropbox to the attacker’s machine.
Note that if you are using behavior analysis, a security analyst could detect the attack in progress by identifying abnormal user behavior.
And that’s exactly what a SOC should do, here, roughly, how the attack could be mitigated: suppose the administrator clicked a link that no one in the company has ever clicked before, then the administrator logged in a particular Dropbox folder at an unusual time. During the final phase of the attack, the attacker’s computer entered the Dropbox folder for the first time. With behavioral analysis, these activities would be flagged as suspicious user behavior.
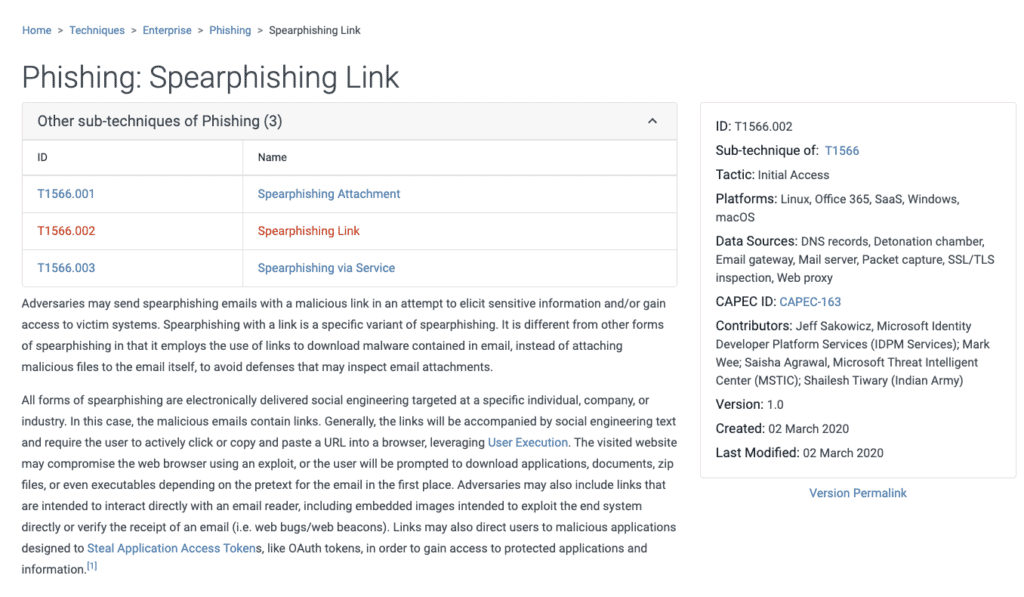
To consult ATT&CK
To consult this resource just visit his site and you will find yourself in front of the matrix of which I published a screenshot a little while ago. Suppose we want to consult the Spearphishing Link technique. By clicking on it, the corresponding page will open containing in-depth information about it, such as a description of the technique, what sub-techniques exist, examples of procedures that include it and suggestions for risk mitigation.
Basically all the information necessary to know and defend oneself appropriately from each technique is available.
Conclusions
The advantages of a resource like MITRE ATT&CK are truly remarkable. Cyber security teams have a valuable ally at their disposal, to which they can add dedicated tools for its consultation.
While it is almost certain that attackers are adapting as defenders deploy new skills, it is also true that ATT&CK provides a way to describe the new techniques they develop.
[btnsx id=”2931″]
Useful links:
Security: Pentest and verification of vulnerabilities
What is a Network Lateral Movement and how to defend yourself
Is SOCaaS useful for your business?
Computer network security: PT vs. VA

In today’s article, we’ll explain what a Security Operations Center (SOC) is and help determine if a SOC-as-a-Service (SOCaaS) solution is right for your business. Just because you have to manage cybersecurity doesn’t mean your business has to deal with cybersecurity. In fact, your core business could be pretty much anything else.
Proper management of IT security, however, is essential to allow your company to grow and to obtain the certifications for data processing required by law. Having the right cybersecurity skills available at the right time is critical to your success, but you have no idea when that time will be.
Choosing the right technology, people and processes to build a modern security operations section is one of the biggest challenges for IT security managers.
What is a SOCaaS and what it can do for you
Before understanding what the management challenges are, it is good to understand what a SOC is. It performs the following functions:
Plan, configure and maintain your security infrastructure.
With a SOC it is possible to configure the technology stack (endpoint, SaaS applications, cloud infrastructure, network, etc.) to identify the relevant activity and eliminate unnecessary data. Monitor data sources to ensure the ecosystem is always connected.
Detect and respond
In addition, it is possible to monitor the incoming alarm activity. Investigate alarms to determine if it is a true security issue or a false alarm. If something is a real security threat, you can evaluate the magnitude of the situation and take response actions.
Threat hunting
The activity of a certain event can be examined to determine if there are any signs of impairment that may have eluded the automated controls. The most common scenario is to review the history of an IP address or file that has been determined to be malicious.
Storage of log files
Another possibility is to securely collect and archive log files, for up to seven years, for compliance with regulations. The team will need to provide this critical data for forensic analysis in the event of a security situation.
Measure performance indicators
Obviously it is possible to monitor the KPIs (performance indicators). In detail it is possible to measure and report the KPIs to demonstrate to the executive team how the SOC is working.
The challenges of implementing your own SOC
Finding, training and retaining cybersecurity professionals is expensive
The skills needed to manage IT security tasks are in high demand. Unfortunately, the shortage is bound to get worse before it gets better. According to the International Certification Organization (ISC), the number of vacant positions worldwide was over 4 million professionals in 2019, up from nearly three million the previous year.
Training personnel with a broad IT background in cybersecurity skills is an option, but retaining these people is expensive. Their replacement, when eventually taken elsewhere, starts a cycle that usually ends up being more expensive than expected, especially compared to SOCaaS.
Also, people who work well in this industry usually want to explore new topics and take on new challenges. You will need to find other related projects or roles to rotate SOC staff to keep them engaged. This also helps build their skills, so they are ready to respond and act promptly when needed.
Cyber security is a team sport
It is important to have a diverse set of skills and a team that works well as a team. Security threats evolve rapidly, proper investigation and responses require people who understand endpoints, networks, cloud applications, and more. Often you end up being a SOC manager, a sysadmin and a threat hunter, depending on the day and what happens in your environment.
This means that you will need a team that is constantly learning, so that you have the right skills when you need them. People who do well in this industry thrive in a team environment where they can learn and challenge each other. For this, you need a workflow that regularly brings together several SOC analysts.
Think of it this way: you wouldn’t put a football team on the pitch that didn’t train together. Your SOC team collides with an opponent who plays as a team every day. To be successful, you need professionals who have a lot of playing experience to build their skills both in the single position and as a team.
A team of SOC analysts who do not do regular training will not be ready when hit by a well-trained opponent. It is difficult to get this experience in a small organization.
A SOCaaS is the immediate answer to this need. The team that will take care of your IT security is trained and stimulated every day by ever new challenges, having to deal with different infrastructures every day.
24/7 coverage is a necessity
Letting an opponent be free to bait for hours, days or weeks makes it infinitely more difficult to contain and remove threats. The adversary knows they have limited time to do as much damage as possible, as in the case of ransomware, or to overshadow ports, as in the case of data extrusion.
You will have the best chance of recovery if you can investigate and respond within minutes. A solution that provides 24 × 7 coverage is therefore essential.
In computer security there are no “working hours” for one particular reason: an attack could come from anywhere on the globe, consequently you cannot rely on conventional hours. This is the result of the spread of the network as an instrument of worldwide connection, we can only deal with it adequately. A SOCaaS relieves the company using it from keeping a division open 24/7.
Managing suppliers and integrating tools is quite expensive
Cyber security is complex and technology evolves rapidly. There will be more and more technologies that need to work together, which requires maintaining the skills to implement, update and configure each component and train your staff on new versions and features. If you have your own SOC, you also need to manage these supplier relationships, licensing, and training.
The bottom line is that building the skills you need requires a lot of low-level tasks and extensive daily work. For organizations that can support it, the effort makes sense. For most organizations, the task is best left to a partner who can provide this service, allowing you to get all the benefits of a high-end SOC without the expense and distraction of building it yourself.
Conclusions
If budget is not an issue and you have enough staff to focus on building and maintaining a 24 × 7 SOC, then it may make sense to go this route. If you are constrained on one of these two fronts, then SOCaaS will be the best approach.
In summary, SOCaaS allows you to:
1. Spend time managing security, not technology and vendors
2. Have a predictable expense. No surprise budget requests
3. Obtain security information from other organizations
4. Manage alarms more efficiently and with more predictable results
5. Be agile and keep up with the IT needs of your evolving organization
6. Stay abreast of today’s security tool innovations.
If your company wants to know more about Secure Online Desktop SOCaaS solutions, contact us for a non-binding consultation. We will show you all the advantages and clear up any doubts regarding this solution.
[btnsx id=”2931″]
Useful links:
Computer network security: PT vs. VA
Cyber Security: Pentest and verification of vulnerabilities

The security of computer networks is of vital importance for a company. With technologies increasingly relying on remote services, it is good to ensure that security is guaranteed. To do this, two tools are used: Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Test. But what is the difference between them? The answer to this question is not as obvious as one might think.
The short answer is: a Pentest (PT) may be a form of vulnerability assessment (VA), but a vulnerability assessment is definitely not a Pentest. Let’s try to better understand how they work and their purposes.
Verification of the security of computer networks: Vulnerability Assessment
A vulnerability assessment is the process of running automated tools against defined IP addresses to identify vulnerabilities in the environment in which one operates. Vulnerabilities typically include unprotected or misconfigured systems. The tools used to perform vulnerability scans are specific software that automates the process. Obviously these software are practically useless without an operator who knows how to use them correctly.
These tools provide an easy way to scan for vulnerabilities and there are both open source and proprietary ones. The main advantage of the open-source ones is that, with great probability, they are the same ones used by hackers, they are unlikely to pay an expensive subscription, when they can download open source applications for free.
In practice, a VA allows you to:
identify and classify security holes in the computer network
understand the cyber threats to which the company is exposed
recommend corrective measures to eliminate the weaknesses found
The purpose of a Vulnerability Assessment is to identify known vulnerabilities so that they can be corrected. Scans are typically done at least quarterly, although many experts recommend monthly scans.
How to perform a VA
Il processo di esecuzione si divide in due fasi e non prevede lo sfruttamento delle debolezze riscontrate. Questo ulteriore passaggio e’ invece previsto nel Penetration Test.
- Fase 1: prima analisi
- durante questa fase vengono raccolte tutte le informazioni disponibili sull’obiettivo per determinare quali potrebbero essere i punti deboli e le falle nel sistema di sicurezza delle reti informatiche
- Fase 2: seconda analisi
- in questa fase, tramite l’uso delle informazioni ricavate, vengono messe alla prova i possibili problemi. In questa fase le vulnerabilita’ sono testate per capire se siano effettivi problemi come supposto precedentemente.
Data l’incredibile velocita’ in cui le tecnologie e le tecniche informatiche si evolvono, e’ possibile che un sistema si mostri sicuro questo mese, ma abbia invece delle criticita’ da risolvere il mese successivo. Per questo e’ consigliato ripetere regolarmente e con frequenza i controlli di sicurezza sulle reti informatiche aziendali.
The execution process is divided into two phases and does not involve exploiting the weaknesses found. This further step is instead foreseen in the Penetration Test.
Phase 1: first analysis
during this phase, all the information available on the objective is collected to determine what could be the weak points and gaps in the security system of computer networks
Phase 2: second analysis
in this phase, through the use of the information obtained, possible problems are put to the test. In this phase the vulnerabilities are tested to understand if they are actual problems as previously assumed.
Given the incredible speed at which computer technologies and techniques evolve, it is possible that a system will prove secure this month, but instead have some problems to solve the following month. For this reason, it is advisable to repeat the security checks on company computer networks regularly and frequently.
Results
At the end of the process of verifying the vulnerabilities of a system, the final reports contain all the results collected. Typically these enclose all relevant information, including:
the list of vulnerabilities found
an in-depth description of the vulnerabilities
countermeasures to be adopted to reduce risks
Verification of vulnerabilities is a fundamental procedure for the company, but it does not guarantee the security of computer networks. For the correct maintenance of the security of your systems, it is also essential to use another tool: the Penetration Test.
Penetration test
The Pentest, or penetration test, is aimed at verifying how the vulnerabilities of a system can be exploited to gain access and move within it. One of the initial steps performed by a pentester is scanning the network to find IP addresses, device type, operating systems and possible system vulnerabilities. But unlike the Vulnerability Assessment, the Pentest doesn’t stop there.
Of crucial importance for a tester is the exploit of identified vulnerabilities in order to gain control of the network or to take possession of sensitive data. The tester uses configurable automated tools to perform exploits against computer network systems. The peculiar part, however, occurs when the tester performs manual exploit attempts, just like a hacker would.
Classification
Penetration tests are classified in two ways: gray box or black box.
Gray box tests are performed with full knowledge of the target company’s IT department. Information is shared with the tester, such as network diagrams, IP addresses, and system configurations. The approach of this method is the verification of the safety of the present technology.
A black box test, on the other hand, represents more properly the action of a hacker who tries to gain unauthorized access to a system. The IT department knows nothing about the test being performed and the tester is not provided with information about the target environment. The black box method evaluates both the underlying technology and the people and processes involved to identify and block an attack as it would happen in the real world.
Phases of the Pentest
Phase 1: Analysis
The system is analyzed, studying its strengths and weaknesses. All preliminary information is collected. This, of course, does not happen if it is a gray box pentest.
Phase 2: Scan
The entire infrastructure is scanned to find the weak points to focus on.
Phase 3: Planning
Thanks to the information gathered, we plan with which tools and techniques to use to hit the system. The possibilities are many and they are both purely technological and social engineering techniques.
Phase 4: actual attack
In this phase the testers try to exploit the identified vulnerabilities to gain full control of the targeted system.
Report
At the end of the Penetration Test, a report is also compiled that details the entire process carried out and includes:
evaluation of the impact of a real attack on the company
solutions to solve problems and secure computer network systems
A Penetration Test that is not successful is a sign that the system under examination is safe * and the data inside it does not risk anything. However, this does not mean that the company will be protected forever from any attack: precisely because the strategies of hackers constantly evolve, it is important to carry out Penetration Tests regularly.
(*) It should be noted, however, that although a good Penetration Test follows guidelines or structuring methodologies (i.e. OWASP) it remains a test with a strong subjective impact of the Penetration Tester and of the team that performed it, therefore it cannot be excluded that by repeating the tests carried out by a different group of Penetration Tester we have no new results. Furthermore, as is well known to our readers, in the field of Cyber Security the concept of “safe” in absolute terms is inadequate.
How to do
Although Vulnerability Assessments and Penetration Tests have different objectives, both should be performed regularly to verify the overall security of the information system.
Vulnerability assessment should be done often to identify and fix known vulnerabilities. The Pentest should be carried out at least once a year and certainly after significant changes in the IT environment, to identify possible exploitable vulnerabilities that may allow unauthorized access to the system. Both of the services described in this article are available through SOD, even on a recursive basis to ensure test effectiveness. contact us to find out more.
[btnsx id=”2931″]
Useful links:
Security: pentest and verification of vulnerabilities
Vulnerability Assessment & Penetration Test
Customers
Twitter FEED
Recent activity
-
SecureOnlineDesktop
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes L'impatto crescente delle minacce informatiche, su sistemi operativi privati op… https://t.co/FimxTS4o9G
-
SecureOnlineDesktop
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes The growing impact of cyber threats, on private or corporate operating systems… https://t.co/y6G6RYA9n1
-
SecureOnlineDesktop
Tempo di lettura stimato: 6 minuti Today we are talking about the CTI update of our services. Data security is… https://t.co/YAZkn7iFqa
-
SecureOnlineDesktop
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes Il tema della sicurezza delle informazioni è di grande attualità in questo peri… https://t.co/tfve5Kzr09
-
SecureOnlineDesktop
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes The issue of information security is very topical in this historical period ch… https://t.co/TP8gvdRcrF
Newsletter
{subscription_form_1}© 2023 Secure Online Desktop s.r.l. All Rights Reserved. Registered Office: via dell'Annunciata 27 – 20121 Milan (MI), Operational Office: via statuto 3 - 42121 Reggio Emilia (RE) – PEC [email protected] Tax code and VAT number 07485920966 – R.E.A. MI-1962358 Privacy Policy - ISO Certifications